Hibernation is a power-saving state designed primarily for laptops. While sleep puts your work and settings in memory and draws a small amount of power, hibernation puts your open documents and programs on your hard disk, and then turns off your computer. Of all the power-saving states in Windows, hibernation uses the least amount of power. On a laptop, use hibernation when you know that you won’t use your laptop for an extended period and won’t have an opportunity to charge the battery during that time.
Turn off hibernation in Windows XP
- Open the Control Panel and access Power Options.
- Select the Hibernate tab in the Power Options Properties dialog box.
- Clear the Enable Hibernation check box and click OK.
Turn off hibernation in Windows Vista, Windows 7
For some reason, turning off hibernation in Windows Vista and Windows 7 is a lot more difficult. The best way to do this is by opening a command prompt in administrator mode.
- Open the Command Prompt window by clicking the Start button, clicking All Programs, clicking Accessories, and then right click on Command Prompt and select “run as administrator”.
- Type in “powercfg.exe -h off” without the quotes (see below).
- Exit the command prompt.
You can also try disabling it in the graphical interface. Note you do not have to do this if you followed the instructions above.
The Hibernate settings are still stored under the Control Panel’s Power Options applet, but they are buried under each power plan’s advanced power settings sub-menu.
- Click start -> control panel.
- Click on power options.
- You should see a screen similar to the one below where you can turn off hibernation.
Turn off hibernation in Windows 8
Turn off hibernation in Windows 10
1) Press Windows key and X at the same time, then choose Command Prompt (Admin) from the list of choice.
When prompted with the User Account Control notification, hit Yes to continue.
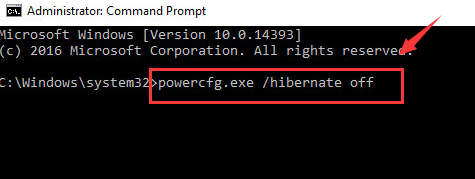
2) In the Command Prompt window, type in the following command:
powercfg.exe /hibernate off and press enter.




Recent Comments